Measuring the Magnitude of Morphological Integration: The Effect of Differences in Morphometric Representations and the Inclusion of Size
Abstract
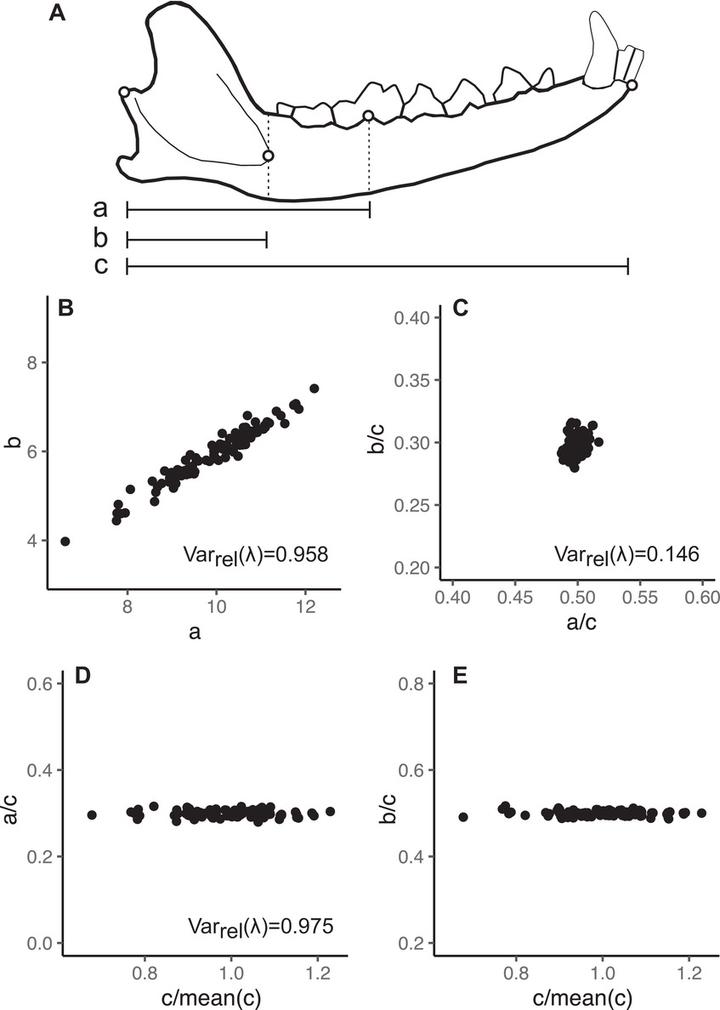
The magnitude of morphological integration is a major aspect of multivariate evolution, providing a simple measure of the intensity of association between morphological traits. Studies concerned with morphological integration usually translate phenotypes into morphometric representations to quantify how different morphological elements covary. Geometric and classic morphometric representations translate biological form in different ways, raising the question if magnitudes of morphological integration estimates obtained from different morphometric representations are compatible. Here we sought to answer this question using the relative eigenvalue variance of the covariance matrix obtained for both geometric and classical representations of empirical and simulated datasets. We quantified the magnitude of morphological integration for both shape and form and compared results between representations. Furthermore, we compared integration values between shape and form to evaluate the effect of the inclusion or not of size on the quantification of the magnitude of morphological integration. Results show that the choice of morphological representation has significant impact on the integration magnitude estimate, either for shape or form. Despite this, ordination of the integration values within representations is relatively the same, allowing for similar conclusions to be reached using different methods. However, the inclusion of size in the dataset significantly changes the estimates of magnitude of morphological integration, hindering the comparison of this statistic obtained from different spaces. Morphometricians should be aware of these differences and must consider how biological hypothesis translate into predictions about integration in each particular choice of representation.